How to Deploy Next.js with GitHub Actions

A bit of context
This is my first technical post, and I want to talk about a topic that gave me quite a few headaches: deploying this portfolio with Next.js. At the end of this article, I’ll share a short reflection, because I found there’s very little documentation on this subject and, on top of that, Vercel doesn’t make it very easy to use Next.js outside of their own platform.
I’d like to give special thanks to Greg Rickaby for his repository nextjs-github-pages, which served as a guide to successfully deploy my portfolio on GitHub Pages.
Steps to Deploy Next.js with GitHub Actions
1. Configure next.config.js
First, make sure to enable output: "export" for static file generation. Also configure basePath with your repository name, and disable image optimization since it only works with SSR (Server-Side Rendering).
import type { NextConfig } from 'next'
const nextConfig: NextConfig = {
output: 'export',
basePath: '/nextjs-github-pages',
images: {
unoptimized: true,
},
}
export default nextConfig
2. Add .nojekyll in the public folder
Create an empty file named .nojekyll inside the public folder. This tells GitHub Pages to disable automatic Jekyll processing, which is necessary for the _next/ directory generated by Next.js to work properly.
3. Adjust image paths with basePath
Any image must include the basePath configured in next.config.js.
<Image
src="/nextjs-github-pages/vercel.svg"
alt="Vercel Logo"
className={styles.vercelLogo}
width={100}
height={24}
priority
/>
// or
<img
src="/nextjs-github-pages/vercel.svg"
alt="Vercel Logo"
className={styles.vercelLogo}
/>
In frameworks like Angular or React, this is handled automatically. Next.js doesn’t solve it yet, so you can create a helper function to simplify it:
const getImagePath = (path: string) => {
return '/nextjs-github-pages/' + path
}
const Foo = () => (
<Image
src={getImagePath('vercel.svg')}
alt="Vercel Logo"
className={styles.vercelLogo}
width={100}
height={24}
priority
/>
)
4. Configure the GitHub Actions workflow
Now let’s set up the workflow that will automate deployment. Create a file in .github/workflows/deploy.yml with the following content:
name: Deploy Next.js site to Pages
on:
push:
branches: ['main']
workflow_dispatch:
permissions:
contents: read
pages: write
id-token: write
concurrency:
group: 'pages'
cancel-in-progress: false
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Detect package manager
id: detect-package-manager
run: |
if [ -f "${{ github.workspace }}/yarn.lock" ]; then
echo "manager=yarn" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "command=install" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "runner=yarn" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
exit 0
elif [ -f "${{ github.workspace }}/pnpm-lock.yaml" ]; then
echo "manager=pnpm" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "command=install" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "runner=pnpm" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
npm install -g pnpm
exit 0
elif [ -f "${{ github.workspace }}/package.json" ]; then
echo "manager=npm" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "command=ci" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
echo "runner=npx --no-install" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
exit 0
else
echo "Unable to determine package manager"
exit 1
fi
- name: Setup Node
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 'lts/*'
cache: ${{ steps.detect-package-manager.outputs.manager }}
- name: Setup Pages
uses: actions/configure-pages@v4
- name: Restore cache
uses: actions/cache@v4
with:
path: .next/cache
key: ${{ runner.os }}-nextjs-${{ hashFiles('**/package-lock.json', '**/yarn.lock') }}-${{ hashFiles('**.[jt]s', '**.[jt]sx') }}
restore-keys: |
${{ runner.os }}-nextjs-${{ hashFiles('**/package-lock.json', '**/yarn.lock') }}-
- name: Install dependencies
run: ${{ steps.detect-package-manager.outputs.manager }} ${{ steps.detect-package-manager.outputs.command }}
- name: Build with Next.js
run: ${{ steps.detect-package-manager.outputs.runner }} next build
- name: Upload artifact
uses: actions/upload-pages-artifact@v3
with:
path: ./out
deploy:
environment:
name: github-pages
url: ${{ steps.deployment.outputs.page_url }}
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
needs: build
steps:
- name: Deploy to GitHub Pages
id: deployment
uses: actions/deploy-pages@v4
Then:
Go to the Settings tab in your repository. Click on Pages. Under Build and Deployment, select GitHub Actions.
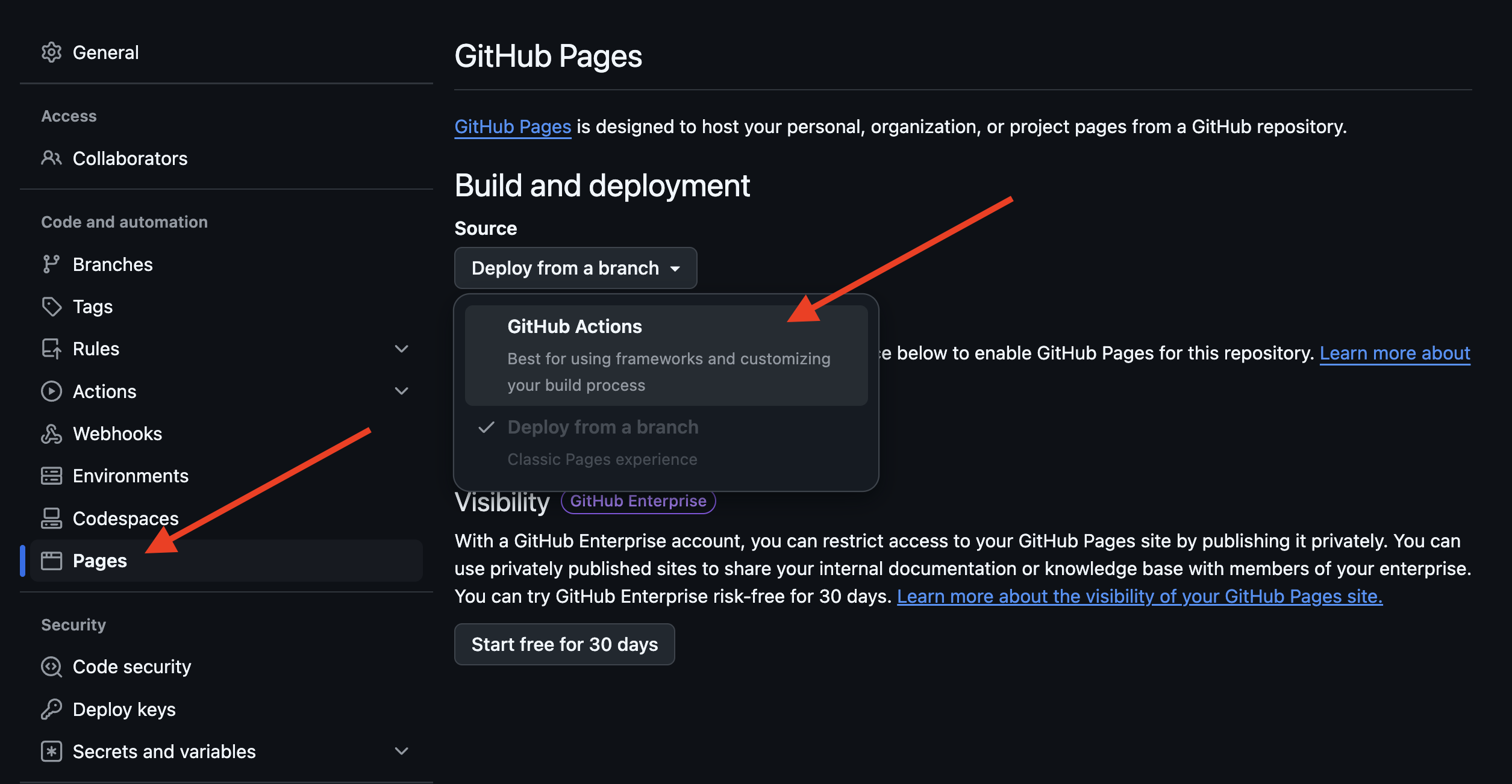
5. Push your changes to GitHub
git add . && git commit -m "initial commit" && git push
And that’s it! Your Next.js application will now be deployed on GitHub Pages.
Things to Keep in Mind
Currently, in the latest version of Next.js, the webpack method in next.config.js does not run inside GitHub Actions.
const nextConfig: NextConfig = {
output: 'export',
basePath: '/nextjs-github-pages',
images: { unoptimized: true },
webpack() {
// This doesn’t work in GitHub Actions
},
}
As a recommendation, avoid relying on webpack() until this issue is resolved.
A Small Reflection
After finishing this deployment, I was left with a clear impression: Next.js is tightly bound to Vercel. The lack of documentation for scenarios outside their platform makes the process more complicated than it needs to be.
In my opinion, the real strength of a framework lies in its flexibility and in providing the best possible developer experience. That’s what enables more people to adopt it.
I hope this article is useful and saves you hours of frustration. Thanks for reading! See you in future posts.
David Alfonso Pereira
07/09/2025